
How to Build GDPR and HIPAA Compliant Dashboards
Data privacy isn’t just a legal concern. it’s a design requirement. As organizations become increasingly data-driven, dashboard creators must prioritize compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Whether you’re handling customer data in Europe or patient data in the U.S., one thing is clear: compliance isn’t optional.
So, how do you build dashboards that deliver insights without risking costly penalties?
Here’s a practical guide.
Why Compliance Matters in Dashboards
- Dashboards centralize sensitive information.
- Visualizing personal or health data can inadvertently expose protected details.
- Non-compliance risks massive fines:
- GDPR: Up to €20 million or 4% of global turnover.
- HIPAA: Fines up to $1.5 million per violation category per year.
From hospitals to retailers, dashboards must be privacy-aware by design.
Understand the Regulations
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
Applies to personal data of EU citizens. Core principles:
- Data minimization
- Purpose limitation
- Transparency
- Right to be forgotten
- Lawful processing (consent, contract, legal obligation, etc.)
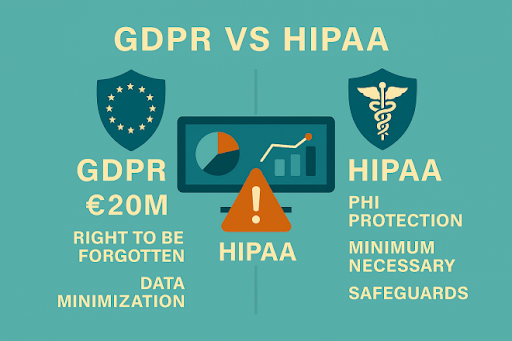
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
Applies to Protected Health Information (PHI) in the U.S. Key requirements:
- Ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI.
- Limit access to minimum necessary data.
- Apply administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
Step-by-Step: Building Compliant Dashboards

- Collect and Store Only Necessary Data
- Avoid importing or visualizing sensitive personal data unless absolutely required.
- Use de-identified or aggregated data wherever possible.
- Apply Data Masking or Anonymization
- Mask names, IDs, addresses, or specific health data when individual identification isn’t needed.
- Use aggregation (e.g., showing counts or averages) instead of exposing raw records.
- Implement Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
- Control who can view sensitive dashboards using platform permissions (e.g., Power BI Row-Level Security).
- Ensure only authorized roles (e.g., compliance officers, clinical staff) can view PHI or PII.
- Audit and Log Data Access
- Enable usage monitoring to track who views or exports sensitive dashboards.
- Retain logs for audits and compliance reporting.
- Label Sensitive Content Clearly
- Apply sensitivity labels (e.g., “Confidential – GDPR” or “Protected Health Data”) on reports and dashboards.
- Use visual cues (icons, headers) to remind users of data sensitivity.
- Use Secure Sharing Channels
- Avoid public links or unsecured exports.
- Share dashboards only through secure, authenticated channels like Microsoft Teams, VPN, or secure email.
- Incorporate Privacy Notices and Disclaimers
- Inform users how data is being processed within the dashboard environment.
- Include links to your organization’s data privacy policies.
- Partner with Compliance Teams
- Engage your data protection officer (DPO) or compliance teams early in dashboard design.
- Schedule regular reviews for ongoing compliance.
Example: GDPR-Compliant Sales Dashboard
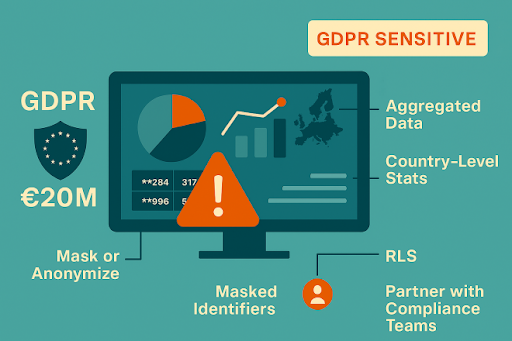
- No customer names or emails displayed.
- Data aggregated at country level (no individual tracking).
- Sensitive fields masked or removed entirely.
- Row-Level Security restricts drilldowns to specific managers.
- Dashboard labeled “GDPR Sensitive – Do Not Share Publicly.”
Result? Actionable insights without exposing PII.
Key Features in Modern BI Tools
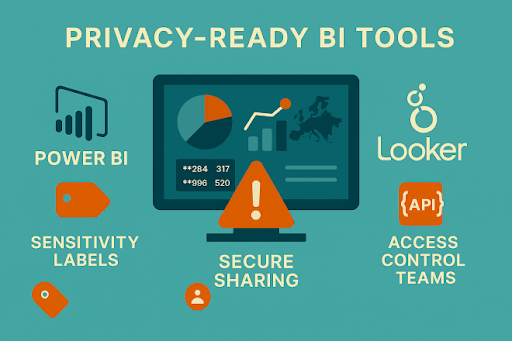
- Power BI: Sensitivity Labels, RLS, Microsoft Purview integration, Azure AD authentication.
- Tableau: Permissions management, anonymized extracts, secure sharing.
- Looker: Data models enforcing access control, API-based governance.
Choose tools with enterprise-grade security and compliance features.
Conclusion: Privacy by Design
GDPR and HIPAA compliance shouldn’t be afterthoughts – they should shape your dashboards from the start. By following Privacy by Design principles, you can:
- Protect sensitive data
- Build trust with customers and stakeholders
- Avoid regulatory penalties
- Enable responsible, ethical data use
In today’s landscape, a compliant dashboard is a smart dashboard.
